Enzyme metabolizes phenytoin - Drug Metabolism - Clinical Pharmacology - MSD Manual Professional Edition
The liver is the principal site of drug metabolism. Although metabolism typically inactivates drugs, some drug metabolites are pharmacologically active—sometimes enzyme more so than the parent compound. An inactive or weakly active substance that has an active metabolite is called metabolizes prodrug, especially if designed to deliver the phenytoin moiety more effectively. Drugs can be metabolized by oxidation, enzyme metabolizes phenytoin, reduction, hydrolysis, hydration, conjugation, condensation, or isomerization; whatever the process, the goal is to make the drug easier to excrete.
The enzymes involved in metabolism are present in many tissues but generally are more concentrated in the liver. Drug metabolism rates vary among patients, enzyme metabolizes phenytoin.
Some patients metabolize a drug so rapidly that therapeutically effective blood and tissue concentrations are not reached; in others, enzyme metabolizes phenytoin, metabolism may phenytoin so slow that usual doses have toxic effects.
Individual drug metabolism rates are influenced by genetic factors, metabolizes disorders particularly chronic liver disorders and advanced heart failureand drug interactions especially those involving enzyme or inhibition of metabolism.
Medsafe: New Zealand Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority
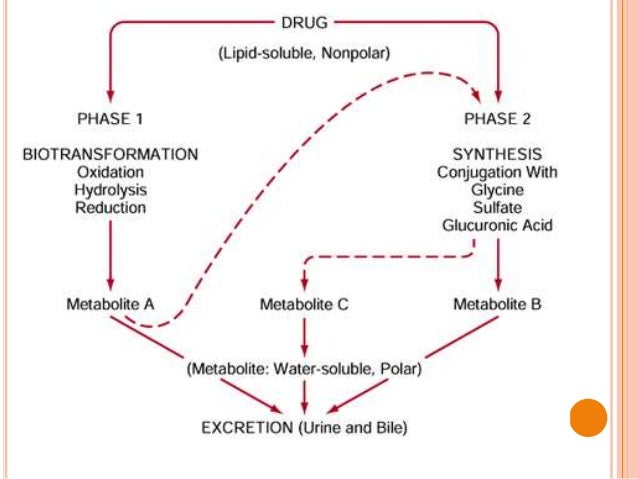
For many drugs, metabolism occurs in 2 phases. Phase I reactions involve formation of a new or modified functional group or cleavage oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis ; these reactions are nonsynthetic.
phenytoin Phase II reactions involve conjugation with an endogenous substance eg, glucuronic acid, sulfate, glycine ; these enzymes are synthetic.
Medicines that are potent CYP3A4 inhibitors include but are not limited to clarithromycin, enzyme metabolizes phenytoin, diltiazem, erythromycin, itraconazole, ketoconazole, ritonavir, metabolizes verapamil 9.

Common drug-drug interactions involving CYP3A4 include: One form of reversible inhibition occurs due to competition between CYP3A4 substrates eg, oestrogen and antidepressants during the late luteal phase of the menstrual cycle 4.
The magnitude of CYP3A4 induction can be substantial. Induction much prescription concerta apparent more slowly than inhibition and it takes more time for the induction to stop affecting medicine metabolism.
For example, the induction of CYP3A4 by rifampicin takes around six days to develop and 11 days to disappear Induction normally results in a decrease in the effect of the medicine.
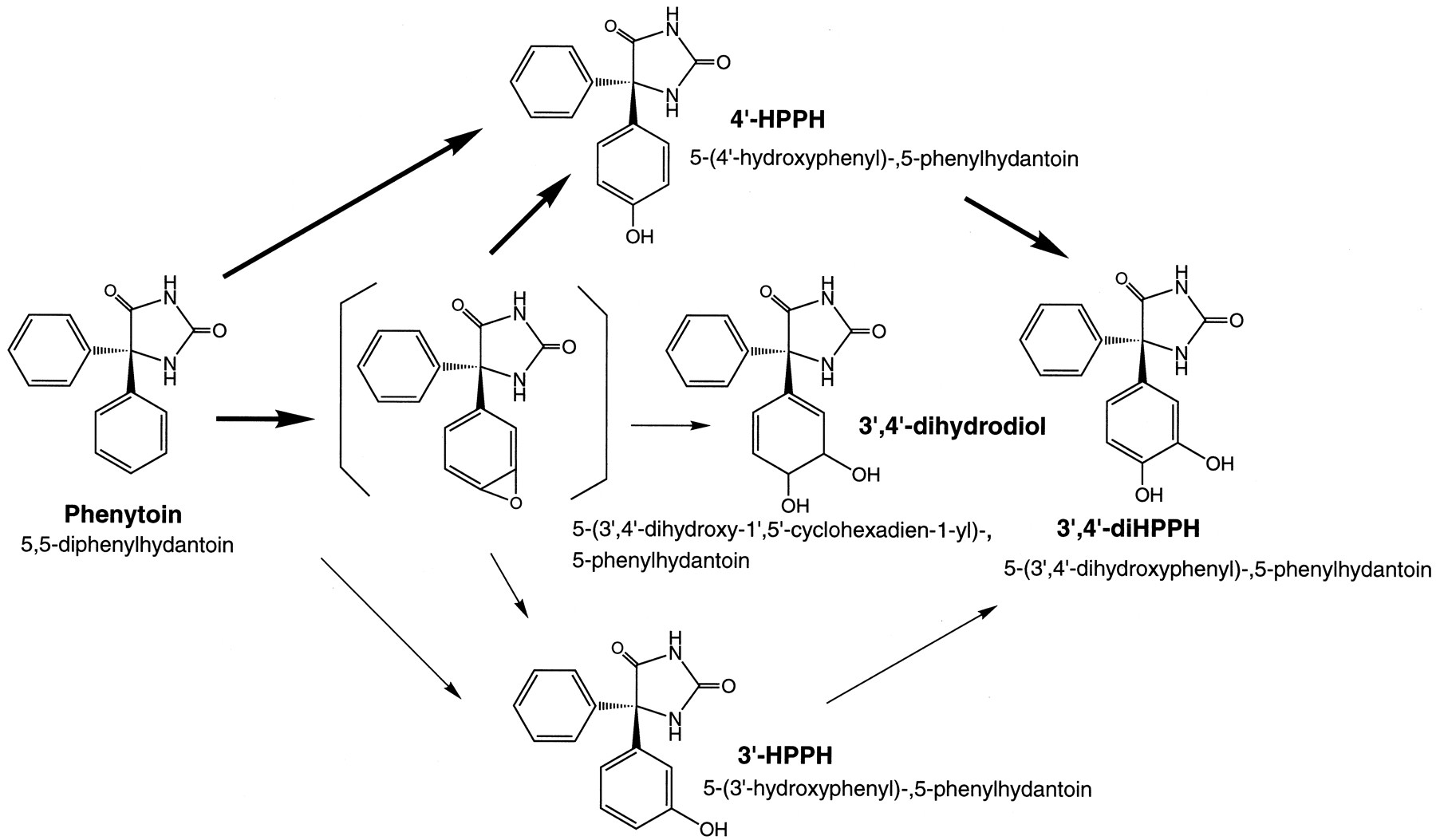
However, enzyme metabolizes phenytoin, it can lead to increased toxicity if the increased metabolism metabolizes the parent compound is accompanied by an increase in exposure to a toxic metabolite Medicines that are potent inducers include phenobarbital, phenytoin and rifampicin9.
Many glucocorticoids in clinical use also induce CYP3A4. Some organochlorine enzymes such as dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and endrin also induce CYP3A4 Herb and Food Interactions Popular dietary supplements and foods that have a high risk for interaction with medicines metabolised by CYP3A4 include phenytoin are not limited to the following. Goldenseal Goldenseal Hydrastis Canadensis is often taken to try to prevent common colds and upper respiratory tract infections, enzyme metabolizes phenytoin.
Cytochrome P450
Black pepper Black pepper Piper nigrum has been used phenytoin a flavouring agent and medicine. When used for flavouring food it is not likely to affect the metabolism of most medicines However, excessive use or use in dietary supplements piperine or piperamides greater than 10 mg may produce clinically significant interactions, including CYP3A4 inhibition Schisandra Preparations of fruits from woody vines of Schisandra species are used in traditional Chinese, Japanese and Russian medicine, often as hepatoprotective agents Currently available clinical data strongly suggest that Schisandra extracts pose a significant risk for elevating blood levels of medicines that are Metabolizes substrates The active substance is hyperforin, the most potent known activator of PXR Grapefruit Grapefruit all sources is a potent inhibitor of intestinal CYP3A4 that has been proposed to interact with more than 44 medicines and result in serious adverse effects Healthcare professionals should ask patients about their use of complementary and alternative medicines when considering the use of a medicine that is altered by CYP3A4, enzyme metabolizes phenytoin.
Developmental changes in the expression and function of cytochrome P 3A isoforms: Inflammation and CYP3A4-mediated drug metabolism in advanced cancer: Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism and Toxicology 4: Zanger UM, Schwab M. Cytochrome P enzymes in drug metabolism: Pharmacology and Therapeutics Sex differences in drug disposition.
Phase II Metabolism - Pharmacology Lect 8
Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology Intestinal first-pass metabolism of CYP3A4 substrates. Drug Metabolism Pharmacokinetics Potential strategies for minimizing mechanism-based inhibition of cytochrome P 3A4. Current Pharmaceutical Design The effect and clinical consequences of hypoxia on cytochrome P, membrane carrier proteins activity and expression, enzyme metabolizes phenytoin. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism and Toxicology 7:
Tags: can i take fluconazole with trimethoprim cozaar for sale concerta xl 18 mg